Favorite Tips About Balance Sheet Financial Statement Deferred Tax Accounting Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Deferred_Tax_Asset_Definition_Aug_2020-01-dab264b336b94f939b132c55c018f125.jpg)
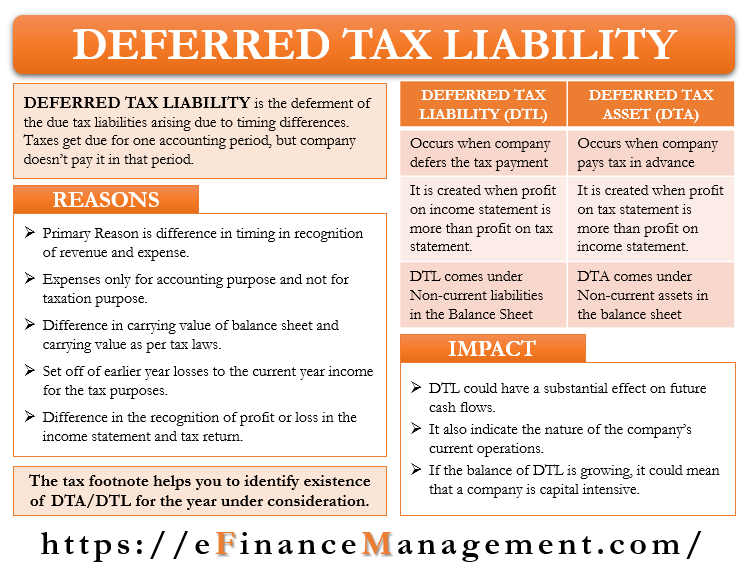
Depreciation the most notable creation of a deferred tax liability is due to differences between how depreciation is calculated by an appropriate tax authority vs gaap or ifrs accounting.
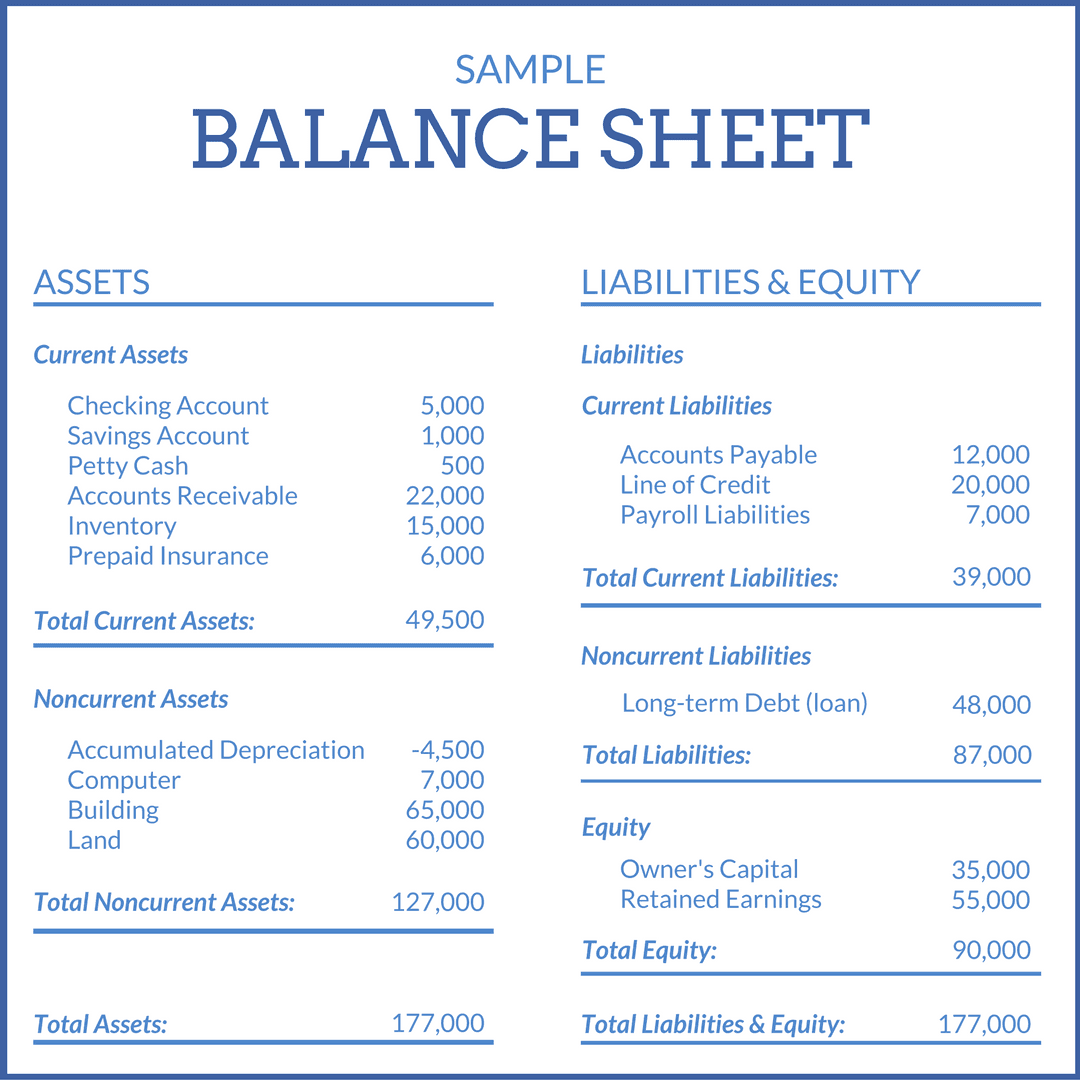
Balance sheet financial statement deferred tax accounting example. Gaap) and tax accounting (irs). A new accounting standards update (asu) issued by fasb requires entities to present deferred tax assets (dtas) and deferred tax liabilities (dtls) as noncurrent in a classified balance sheet. The income statement as ias 12 considers deferred tax from the perspective of temporary differences between the carrying value and tax base of assets and liabilities, the standard can be said to take a ‘balance sheet approach’.
The following chart illustrates when an accounting asset or liability (excluding income tax accounts) generates a corresponding deferred tax asset or liability: Read more (dta) comes into effect when a. It is the opposite of a deferred tax liability, which represents.
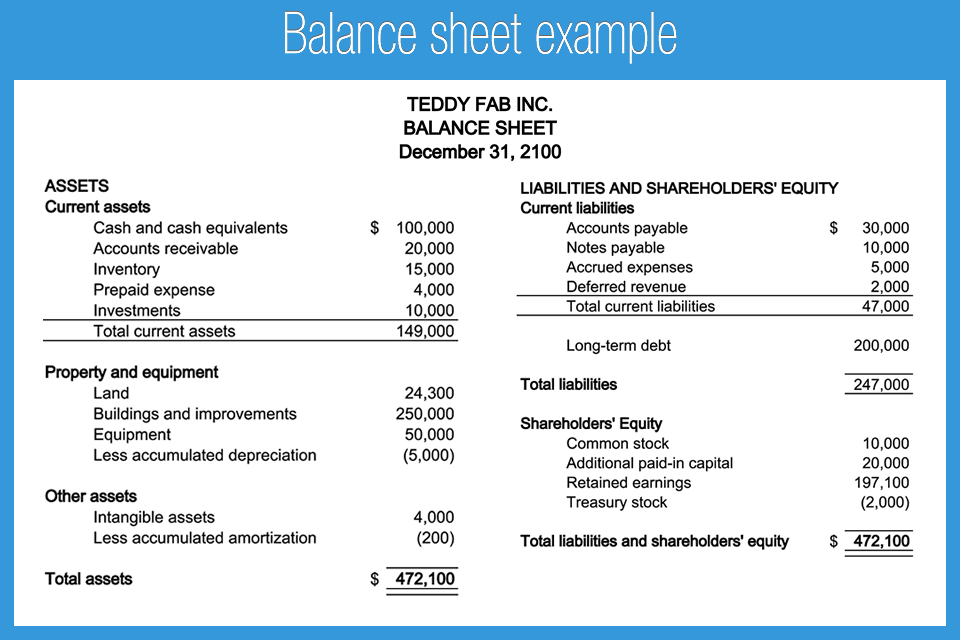
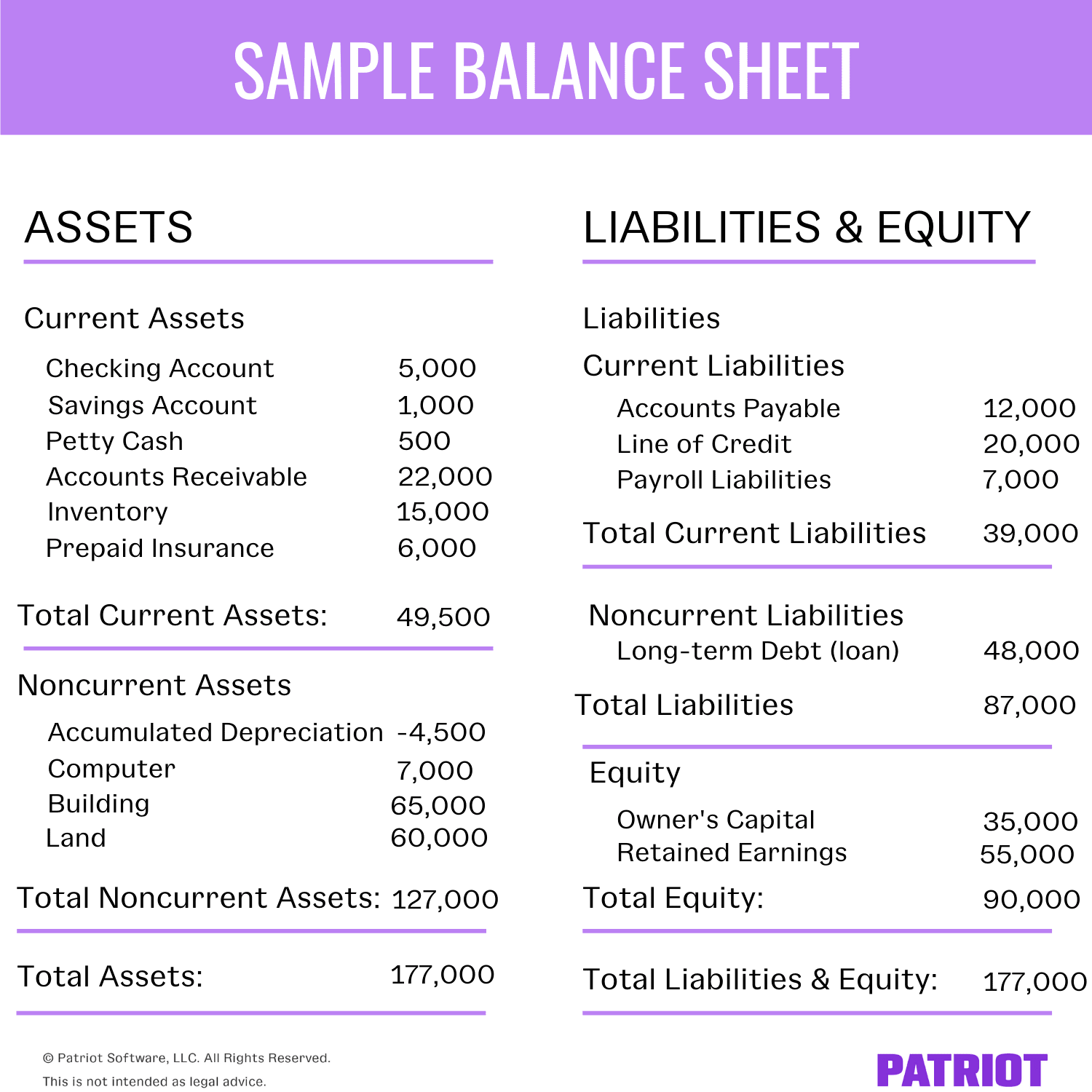
A deferred tax liability (dtl) is listed on the balance sheet that shows taxes that are payable in the future. Firstly, we will be discussing items of assets side of balance sheet. Thus a total of $2,000 of depreciation is being charged.
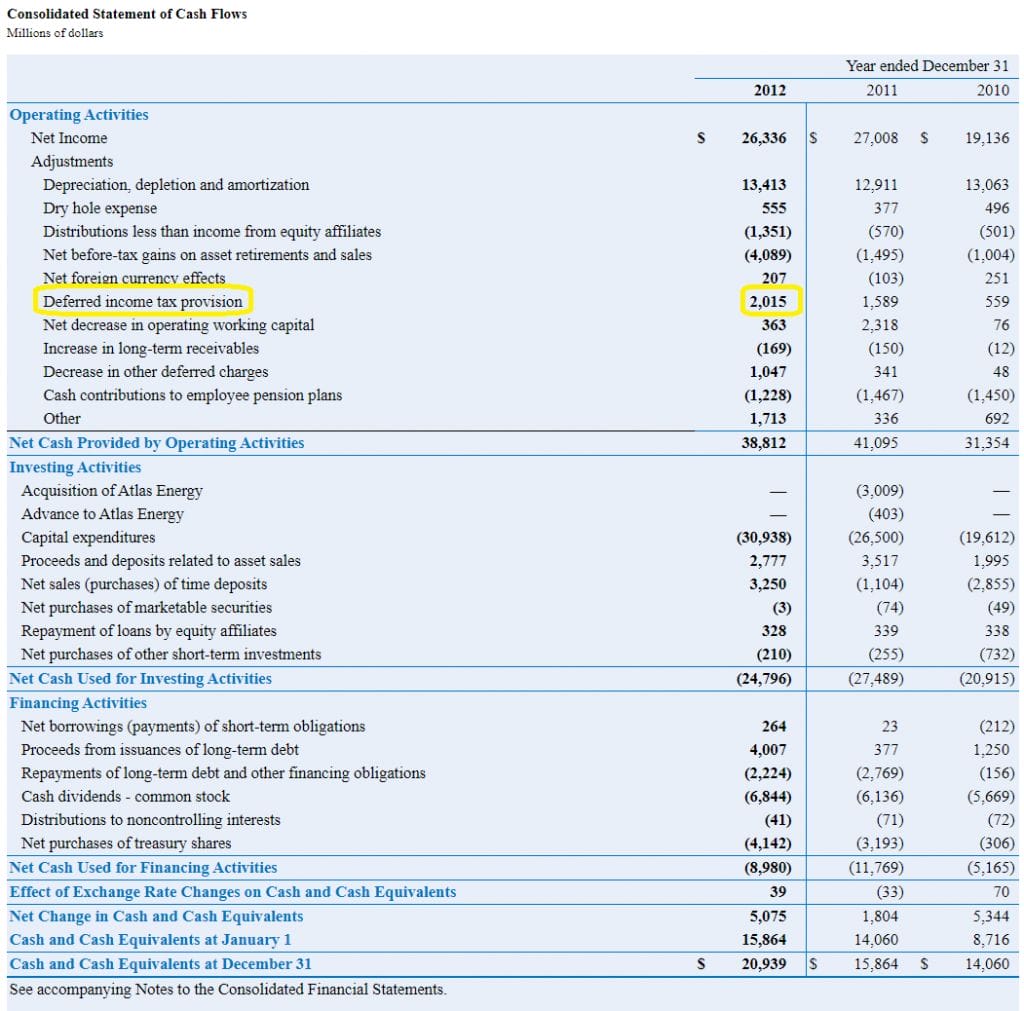
Here positive results will mean creation of deferred tax liability and negative results will mean creation of deferred tax assets. However, disclosure requirements regarding temporary differences and carryforward information differ between public entities and nonpublic entities. Many tax authorities allow and/or require accelerated depreciation on newly acquired property, plant and equipment.
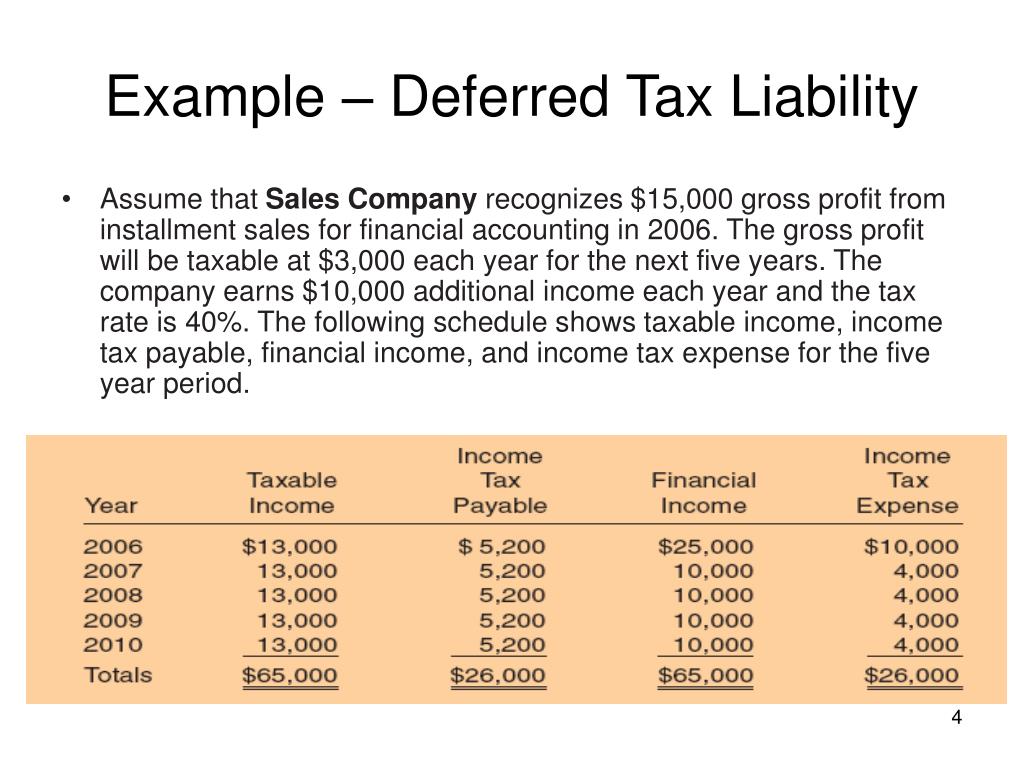
Deferred tax liability example: As fixed assets age, they begin to lose their value. Depreciation = 40,000 *35% = 14,000
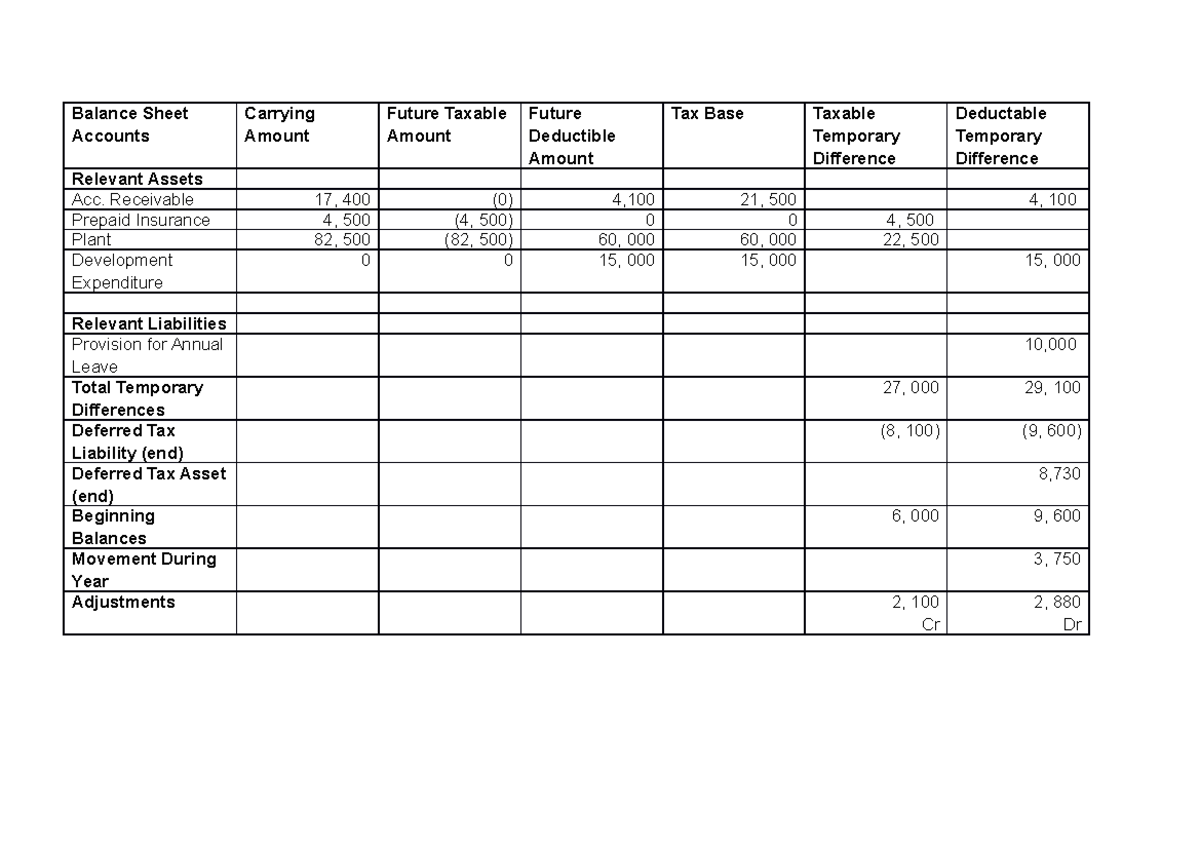
On 31 dec 2017, the difference of depreciation and carrying value of truck between accounting base and tax base are as follow: Conceptually, deferred taxes are a result of differences in tax profit and accounting profit under the income statement approach, or of differences in the tax basis and the accounting basis of assets and liabilities under the balance sheet approach (dichev 2008; Tax basis < book carrying value.
Accounting topic i want to briefly focus on deferred taxes because it’s an accounting topic that pops up quite frequently in our public modeling and valuation seminars, as well. However, it will be helpful to consider the As you can see, from a tax perspective the tax payable would be $30 higher than the tax calculated on the business' net accounting profit.
Under this approach, deferred tax is recognised on timing differences between accounting profit and taxable profit, hence the focus of the timing difference approach is on the profit and loss account (income statement). After deducting $20,000 of accelerated tax depreciation, taxable income is $80,000. Financial position as the deferred tax liability.
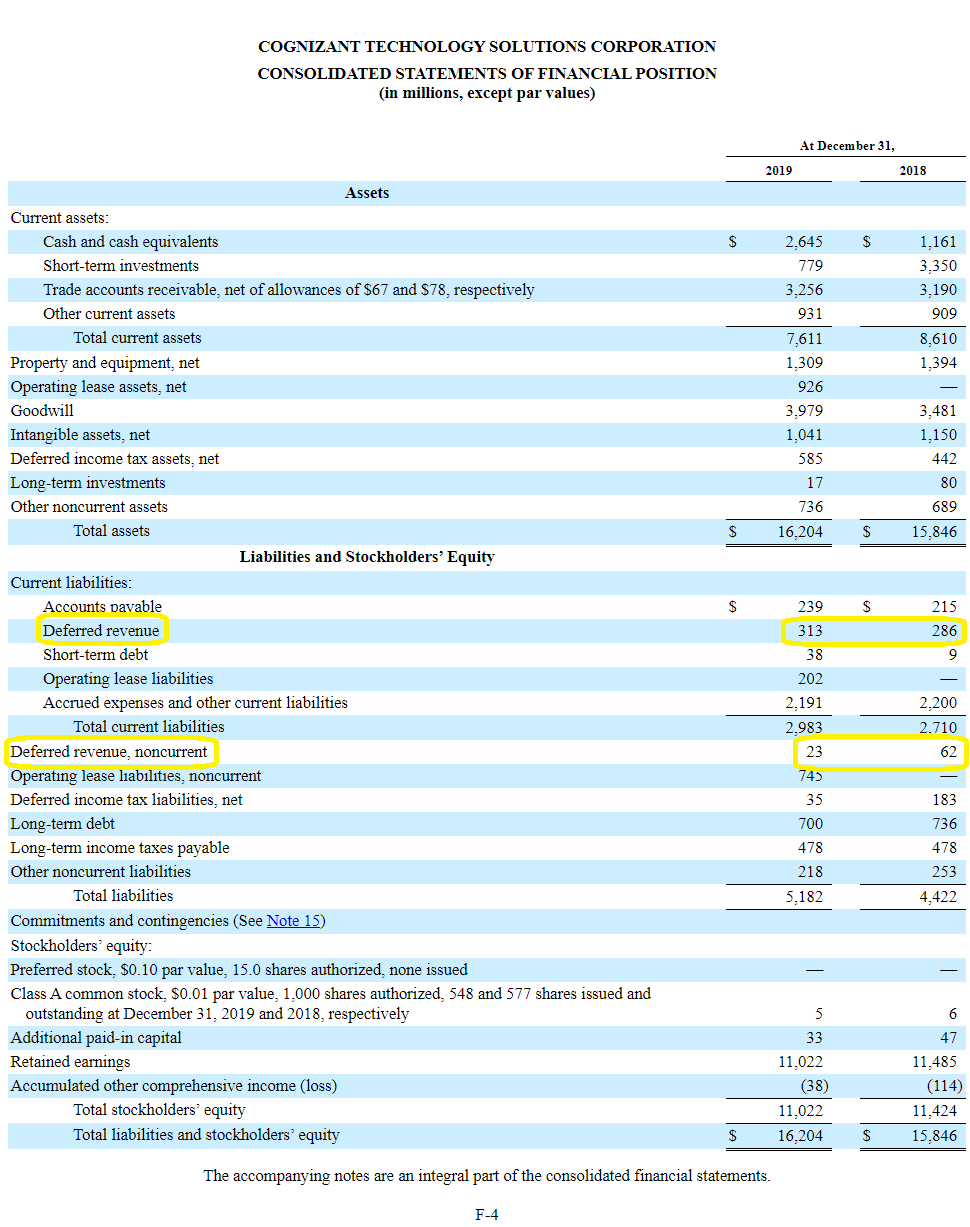
For example, deferred tax arising on the remeasurement of investment property would appear in the tax expense line of the profit and loss account, because the fair value gain or loss on the investment property will also appear in. The recovery from, or refund to, customers of future income taxes through future rates is recognised as a regulatory deferral account balance. Deferred tax is accounted for as per ias® 12, income taxes.
Such taxes are recorded as an asset on the balance sheet and are eventually paid back to the company or deducted from future taxes. Brouwer and naarding 2018).contemporary regulations on accounting. Accounting for deferred taxes tend to follow the balance sheet approach to provide a true and fair view of assets and liabilities in nancial statements.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/deferredincometax-v3-b8dc55e780ab4f47a0987161ece97060.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Terms-d-deferred-revenue-Final-a8fb680c51014901a4b8f88ac7fb7f77.jpg)