Out Of This World Tips About Contingent Liabilities Note Disclosure Example

You can learn more about.
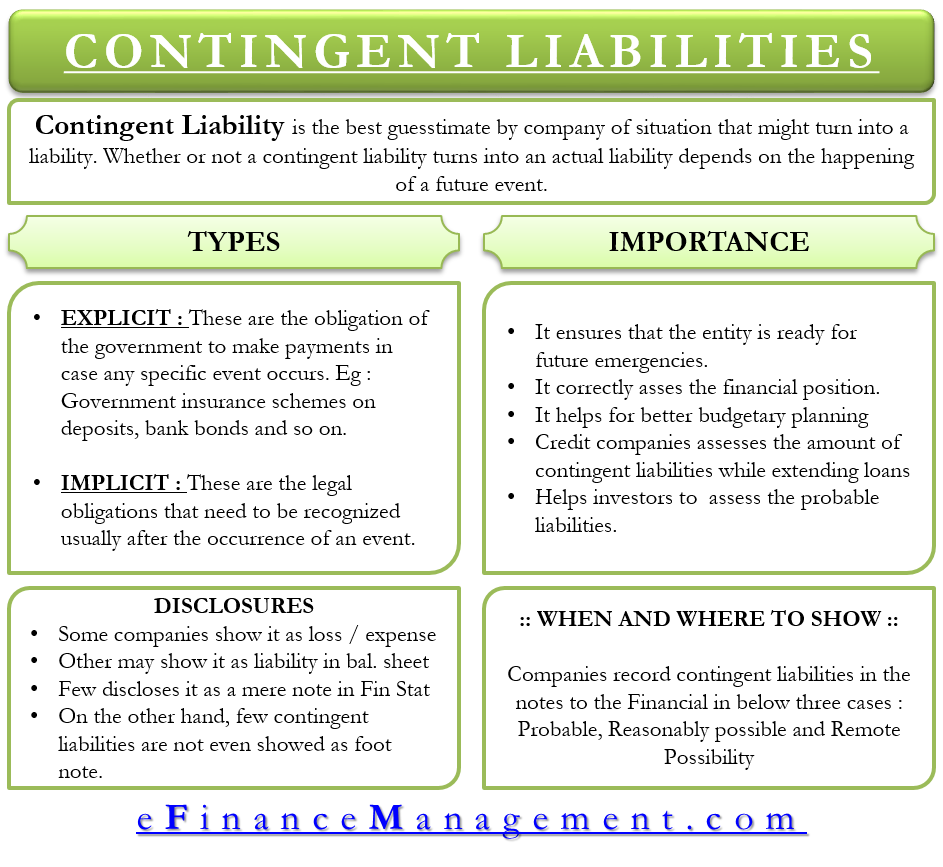
Contingent liabilities note disclosure example. We explain it with example, differences with provisions, disclosure & types. Contingent consideration arrangements (asset or liability) and indemnification assets:.
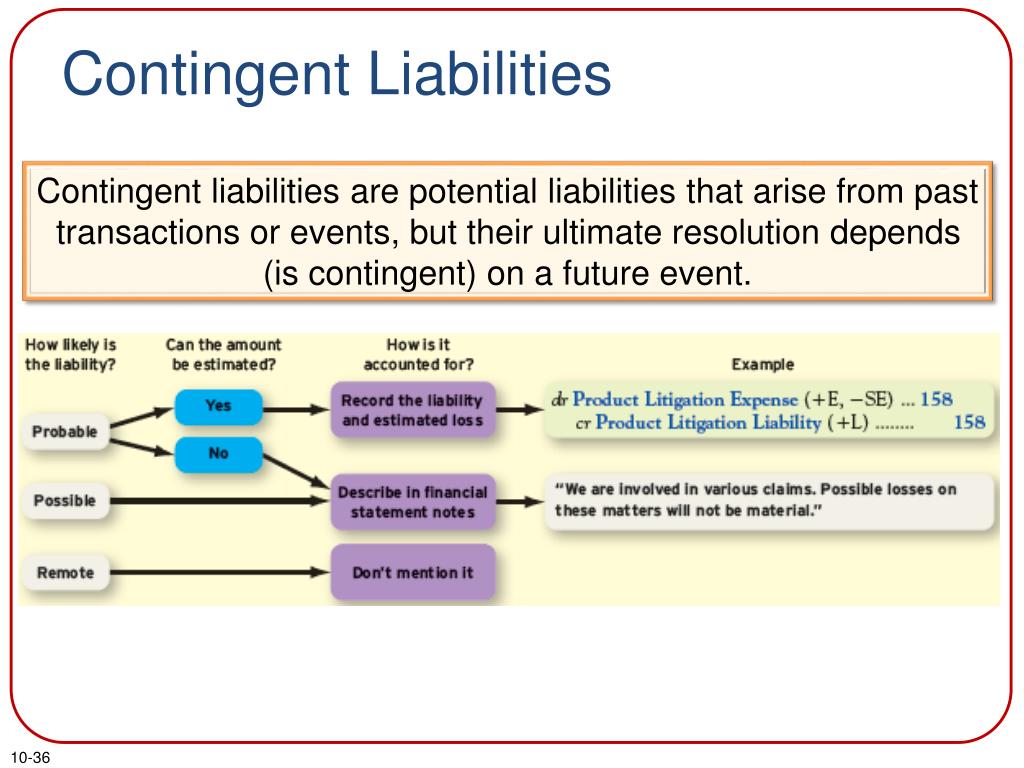
In reporting period when the. An example is a claim against an entity if the entity concludes that it is liable but that it is likely to defend the case successfully.
Other examples include guarantees on debts, liquidated damages, outstanding lawsuits, and government. This chapter gives a comparison of frs. In the notes to the financial statement:
Contingent liabilities and contingent assets in the notes to the financial statements, to enable users to understand their nature, timing, and amount. The contingent liabilities recognized in connection with the diesel issue totaled €4.2 billion (previous year: It is a present obligation, but its.
The most common example of a contingent liability is a product warranty. For each class of contingent liability, unless the possibility of an outflow of economic benefits is remote, the following must be disclosed: Fully updated guide focusing on each area of the financial statement in detail with illustrative examples.
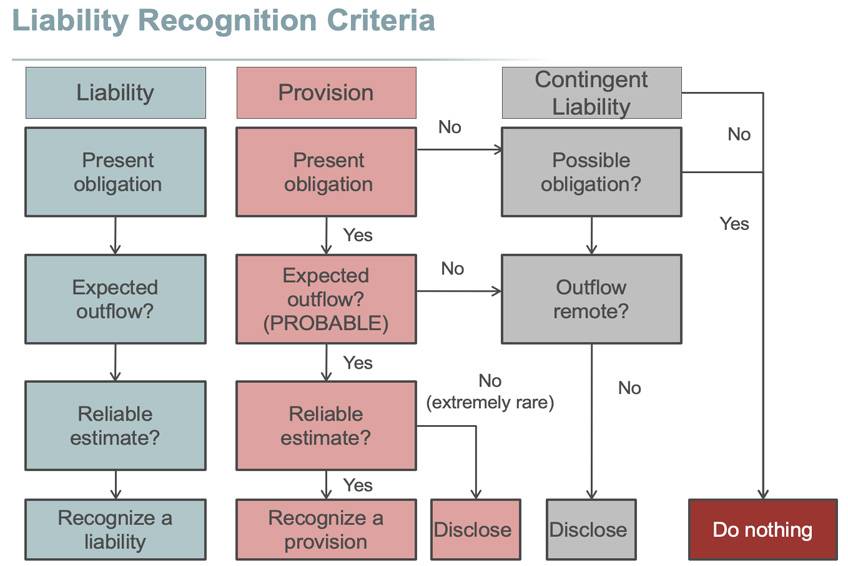
This article has been a guide to contingent liabilities and their meaning. Measurement bases are applied to provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets and that sufficient information is disclosed in the notes to enable users to understand. Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible.
Contingent liabilities are possible obligations whose existence will be confirmed by uncertain future events that are not wholly within the control of the. Financial effects of provisions and the disclosure of contingent liabilities and contingent assets: (a) for each class of provision, an entity.
Both represent possible losses to the company, and. Contingent liabilities would include, but are not limited to: Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible.
Disclosure of contingent liabilities contingent liabilities aren’t recognised in the primary financial statements but should be disclosed in the notes. In1 hkas 37 prescribes the accounting and disclosure for all provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets, except:





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contingentliability-Final-84e09f386f114ab0b786c4a2ad5bad18.jpg)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contingentasset-Final-6926122bf7e14c2e95f9bad4e4bc69fe.png)